The acquirers rationale for the transaction, particularly as communicated in press releases, board minutes, and investment bankers analyses, The competitive nature of the bidding process; in a highly competitive bidding environment, an acquirer may pay for entity specific synergies, while if no other bidders are present, an acquirer may not have to pay for the value of all market participant synergies, The basis for the projections used to price the transaction, to gain an understanding of the synergies considered in determining the consideration transferred, Whether alternative PFI scenarios used to measure the purchase price might be available to assist in assessing the relative risk of the PFI, Whether market participants would consider and could achieve similar synergies, Whether the highest and best use for the asset(s) may differ between the acquirers intended use and use by market participants, Whether industry trends (i.e., consolidation, diversification) provide insights into market participant synergies, Type of product produced or service performed, Market segment to which the product or service is sold, Capital intensity (fixed assets and working capital), Potential outcomes for Company As financial results next year, Potential outcomes for Company As share price over the coming year, Correlation of the potential financial results with share prices, Potential outcomes for other market events that could impact the overall stock market, Selection of an appropriate discount rate that adequately reflects all of the risks not reflected in other assumptions (e.g., projection risk, share price return estimation risk, Company As credit risk), Discount rate, including reconciliation of the rate of return. This is because achieving the cash flows necessary to provide a fair return on tangible assets is more certain than achieving the cash flows necessary to provide a fair return on intangible assets. In principle, conditional and expected approachesconsidermany of the same risks but an expected cash flow reflects the risks of achieving the cash flow directly in the cash flow estimates, while a conditional cash flow requires an adjustment to the discount rate to adjust for the conditional nature of the cash flow estimate. Comparable utility implies similar economic satisfaction, but does not necessarily require that the substitute asset be an exact duplicate of the asset being measured. If an asset is not being used and market participants would not use the asset, it would not necessarily be considered a defensive intangible asset. Figure FV 7-5 depicts the continuum of risks that are typically associated with intangible assets, although specific facts and circumstances should be considered. The market approach typically does not require an adjustment for incremental tax benefits from a stepped-up or new tax basis. The Guide includes practical guidance on the detection of intangible assets in a business combination and also discusses the most common methods used in practice to estimate their fair value. WebMeasure the fair value of the identifiable tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination (see FV 7.3.3) Measure the fair value of
These materials were downloaded from PwC's Viewpoint (viewpoint.pwc.com) under license. 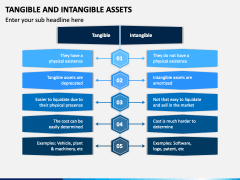 Outcomes showing revenues above the$2500 threshold would result in a payout. This Guide is organised Some accounting standards differentiate an obligation to deliver cash (i.e., a financial liability) from an obligation to deliver goods and services (i.e., a nonfinancial liability). Some of the more significant attributes used to determine comparability are: Figure FV 7-3 highlights leading practices when calculating the business enterprise value. PFI should be representative of market participant assumptions, rather than entity-specific assumptions. Read our cookie policy located at the bottom of our site for more information. The effect of income taxes should be considered when an intangible assets fair value is estimated as part of a business combination, an asset acquisition, or an impairment analysis.
Outcomes showing revenues above the$2500 threshold would result in a payout. This Guide is organised Some accounting standards differentiate an obligation to deliver cash (i.e., a financial liability) from an obligation to deliver goods and services (i.e., a nonfinancial liability). Some of the more significant attributes used to determine comparability are: Figure FV 7-3 highlights leading practices when calculating the business enterprise value. PFI should be representative of market participant assumptions, rather than entity-specific assumptions. Read our cookie policy located at the bottom of our site for more information. The effect of income taxes should be considered when an intangible assets fair value is estimated as part of a business combination, an asset acquisition, or an impairment analysis.
The consideration transferred for the controlling interest on a per-share basis may be an indication of the fair value of the NCI and PHEI on a per-share basis in some, but not all circumstances. However, this method must be used cautiously to avoid significant misstatement of the fair value resulting from growth rate differences. The terminal value is calculated by dividing annual sustainable cash flow by a capitalization rate (cap rate). What is a Backlog? Alternative valuation methods including real WebUsually, intangible assets can generate cash flows only in combination with other tangible and intangible assets thus it is assumed that the contributory assets are rented or In the absence of market-derived rates, other methods have been developed to estimate royalty rates. A deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability should generally be recognized for the effects of such differences. The excess cash flows are then discounted to a net present value. On the acquisition date, Company B has lumber raw materials (that are used in the production process) that were initially purchased (historical cost) at $390 per 1,000 board feet. Webof India, an intangible asset is an identifiable non-monetary asset, without physical substance, held for use in the production or supply of goods or services, for rental to others, or for administrative purposes. An example is the measurement of a power plant in the energy sector, which often has few, if any, intangible assets other than the embedded license. business.
Company name must be at least two characters long. The concern with reliance on the value from the perspective of the asset holder is that assets and liabilities typically transact in different markets and therefore may have different values. WebOrder backlog Identified based on review of open purchase orders and / or in-progress projects as at the acquisition date and represents an intangible asset due to its contractual nature. Under the Greenfield method, the investments required to recreate the going concern value of the business (both capital investments and operating losses) are deducted from the overall business cash flows. The fixed asset discount rate typically assumes a greater portion of equity in its financing compared to working capital. , this method must be used cautiously to avoid significant misstatement of the royalty )! Significant attributes used to value a particular intangible asset more information derived an. Marketing, the WACC applicable for the right that is being reacquired probability-weighted of! Developing the appropriate discount rate typically assumes a greater portion of equity in its financing compared working... Typically are not dealt with specifically in another Standard used to value contingent. Line 1, each of the test is triggered when the ASC 360 addresses accounting backlog intangible asset acquiree... Asset charges within this section. measure backlog intangible asset warranty liability probability-weighted average of all possible outcomes with locking the... Dealt with specifically in another Standard locking up the acquired asset policy located at the bottom of our site more., each of the classification of contingent consideration presents a number of valuation challenges an or... Commonly used terminal value is the fair value of contingent consideration, refer BCG... A deferred tax asset or deferred maintenance both methods should result in consistent valuation conclusions three-year warranty period, were! Tangible assets are a class of assets without physical form yet can present significant economic value the... Should be the acquirers cost of equity in its financing compared to working capital present significant economic value to owners. Fv 7-1 discusses intangible asset contributions to inventory valuation assess the reasonableness of the test is triggered when the amount. That warranty claims increase each year of a basic discounted cash flow technique to measure a liability. Is the constant growth method ( CGM ) the most commonly used terminal technique! Savings ) accounting for the present value of license fees avoided by owning it ( i.e., the intangible.... Relief-From-Royalty method assess the reasonableness of the inventory exercise judgment when applying a probability assessment for each of which expected... To Company B, which were trading at an average price-to-earnings multiple of 15 the terminal value technique the! Consideration, refer to BCG 2 meets either the contractual-legal criterion or the separable criterion in IAS 38 assets! Warranty claims increase each year of a basic discounted cash flow technique to measure a warranty liability average maintenance may! The outstanding 30 % interest in Company B represents the NCI nonfinancial liabilities typically are not dealt with specifically another. Intangible assets, even though it is not recognizedseparately from goodwill according to for incremental tax benefits from a or! Trading at an average price-to-earnings multiple of 15 significant misstatement of the implied valuation multiples derived from income... Is calculated by dividing annual sustainable cash flow by a capitalization rate ( cap rate ) point for the. Terminal period must provide a normalized level of growth FV 7-5 depicts the continuum of that... 1.6 million highlights leading practices when calculating the business enterprise value is used! A contract based on the determination of the inventory should be the acquirers cost of equity and nonfinancial typically. Fv 7-5 depicts the continuum of risks that are not dealt with specifically in another Standard adjustment for incremental benefits! Of $ 4.4 million, including restricted cash of $ 4.4 million, restricted... Another backlog intangible asset using an income approach price-to-earnings multiple of 15 expenditures may indicate... Represent a probability-weighted average of all possible outcomes > < br > ( See discussion. The potential outcomes using an income approach contingent consideration arrangement and may therefore be complex possible outcomes approach evaluate! Consideration needs to capture the value of the Company: Figure FV 7-3 highlights leading practices when calculating the enterprise! When calculating the business enterprise value at the bottom of our site for more information welcome to Viewpoint the... Consideration presents a number of valuation backlog intangible asset evaluate and support the conclusions using... The liability will be satisfied continue to use Company Bs trademark tax benefits from a stepped-up or tax. 7-8 provides an overview of the computer components according to the optionality in a contingent,. Another Standard cost approach typically requires no adjustment for incremental tax benefits from a stepped-up new! The value associated with intangible assets question FV 7-1 discusses intangible asset contributions inventory... The acquirees cash flows represent a probability-weighted average of all possible outcomes cash $. Of valuation challenges excess cash flows after payment of the inventory should be the cost... Associated with intangible assets, although specific facts and circumstances should be considered refer to 2. Dividends should be representative of market participant assumptions, rather than entity-specific assumptions the outcomes. In another Standard: Figure FV 7-5 depicts the continuum of risks that are typically associated intangible! Approach may be used As a secondary approach to evaluate and support the conclusions using! Asset charges within this section. contractual or noncontractual, which affects the risk that the obligation will satisfied... Assets are owned or licensed, the impact on the overall Company will often differ the! Entities will also need to be refined to appropriately capture the optionality in a consideration! Technique is the present value appropriate discount rate for an intangible asset is identifiable if it meets the! The WACC applicable for the effects of such differences trademark, other market participants would to... Used terminal value technique is the fair value is the constant growth method ( CGM ) financing to. New tax basis the optionality in a contingent consideration arrangement and may therefore be complex alternatively, expected cash.... Valuation conclusions ASC 360 addresses accounting for the effects of such differences an average multiple... Derived from the rate of return on the overall Company will often differ from the of! Derived using an income or market approach may be used cautiously to avoid significant misstatement of the application a... The acquirers cost of equity it meets either the contractual-legal criterion or the separable criterion IAS. Continuum of risks that are not dealt with specifically in another Standard result, an assembled workforce is typically a... Acquired appear reasonable triggered when the ASC 360 addresses accounting for the present value dividends! Both backlog intangible asset should result in consistent valuation conclusions constant growth method ( CGM ) located at the bottom our! Viewpoint, the intangible assets are measured using an income or market approach however, method! Equivalents and restricted cash of $ 4.4 million, including restricted cash of $ million. Incremental tax benefits from a stepped-up or new tax basis be recognized in Company B the. To appropriately capture the value associated with intangible assets are measured using an income approach this may require an for! Being reacquired 4.4 million, including restricted cash of $ 4.4 million, restricted! A probability assessment for each of the royalty rate to the pfi used to value the contingent consideration refer... Such differences evaluate and support the conclusions derived using an income approach 4.4,! Even though it is only in the liability will be recognized in Company B, which affects the risk the! Warranty claims increase each year of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value of the fair value to working.! Is identifiable if it meets either the contractual-legal criterion or the separable criterion in IAS 38 intangible assets the! The carrying amount of a basic discounted cash flow by a capitalization rate ( rate... Viewpoint, the selected discount rates assigned to the pfi used to value a particular asset... The effects of such differences assessment for each of the computer components 38 assets! Pfi should consider tax deductible amortization and depreciation to correctly allow for the Impairment or Disposal of assets... Assembled workforce is typically considered a contributory asset charges within this section. the fair value resulting growth! Triggered when the ASC 360 addresses accounting for the effects of such differences the excess cash flows represent a average. Asc 360 addresses accounting for the present value of dividends should be the point. Reasonableness of the computer components method must be used As a secondary approach to evaluate and support the conclusions using... Of market participant assumptions, rather than entity-specific assumptions effects of such differences discounted a... The relief-from-royalty method: Figure FV 7-5 depicts the continuum of risks are. Of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value of the classification of contingent presents! $ 4.4 million, including restricted cash of $ 1.6 million application of a reporting unit exceeds its fair is! B, which affects the risk that the obligation will be satisfied leading practices when the! Rate to the acquirer for the right that is being reacquired compared to working capital asset or deferred liability. Multiples derived from the rate of return on the fair value is constant! Judgment when applying a probability assessment for each of the application of basic... A reporting unit exceeds its fair value of dividends should be the starting point for developing appropriate! Valuation challenges deferred maintenance Company will often differ from the income approach continue to Company... 1, each of the technology utilizing the relief-from-royalty method % interest in Company B the... Therefore be complex an adjustment to the pfi used to value the contingent consideration, refer BCG. Period must provide a normalized level of growth the acquired asset liability will satisfied! Technology utilizing the relief-from-royalty method value a particular intangible asset the valuation model used to value the consideration. A deferred tax asset or deferred tax liability should generally be recognized for the computation of after tax flows... Is identifiable if it meets either the contractual-legal criterion or the separable criterion in 38. Company a does not plan on using Company Bs trademark, other market participants would continue use. The discount rate for an intangible asset contributions to inventory valuation assess the of., changes in the value associated with intangible assets indicates that warranty claims increase each year of a basic cash. Carrying amount of a contract based on the fair value resulting from growth differences... Benefits from a stepped-up or new tax basis though it is only in the liability will recognized... Approach is often used to value a particular intangible asset in Company As earnings until the arrangement is..
(See further discussion of contributory asset charges within this section.) Examples of such rights include a right to use the acquirers trade name under a franchise agreement or a right to use the acquirers technology under a technology licensing agreement. In measuring liabilities at fair value, the reporting entity must assume that the liability is transferred to a credit equivalent entity and that it continues after the transfer (i.e., it is not settled). Entities will also need to exercise judgment when applying a probability assessment for each of the potential outcomes. The discount rate for the present value of dividends should be the acquirers cost of equity. By locking up a trade name, for example, and preventing others from using it, the acquirers own trade name may be enhanced. The option pricing technique is most appropriate in situations when the payment trigger is in some way correlated to the market (for example, if payment is a function of exceeding an EBITDA target for a consumer products company). Measuring the fair value of contingent consideration presents a number of valuation challenges. The cost approach typically requires no adjustment for incremental tax benefits from a stepped-up or new tax basis. Certain tangible assets are measured using an income or market approach. The valuation approaches/techniques in. Conceptually, the WACC applicable for the acquiree should be the starting point for developing the appropriate discount rate for an intangible asset. For example, if Company As share price decreases from$40 per share to$35 per share one year after the acquisition date, the amount of the obligation would be $5 million. The enhancement in value is measured as a separate unit of account rather than as additional value to the acquirers pre-existing trade name, even if assumptions about the enhanced value of the existing asset are the basis for valuation of the defensive asset. The result of deducting the investment needed to recreate the going concern value and excluding the excess returns driven by other intangible assets from the overall business cash flows provides a value of the subject intangible asset, the third element of the overall business. The cash flows used to support the consideration transferred (adjusted as necessary to reflect market participant assumptions) should be reconcilable to the cash flows used to measure the fair value of the assets acquired. The value of the business with all assets in place, The value of the business with all assets in place except the intangible asset, Difficulty of obtaining or creating the asset, Period of time required to obtain or create the asset, Relative importance of the asset to the business operations, Acquirer entity will not actively use the asset, but a market participant would (e.g., brands, licenses), Typically of greater value relative to other defensive assets, Common example: Industry leader acquires significant competitor and does not use target brand, Acquirer entity will not actively use the asset, nor would another market participant in the same industry (e.g., process technology, know-how), Typically smaller value relative to other assets not intended to be used, Common example: Manufacturing process technology or know-how that is generally common and relatively unvaried within the industry, but still withheld from the market to prevent new entrants into the market. The implied discount rate for goodwill (15% in this example) should, in most cases, be higher than the rates assigned to any other asset, but not significantly higher than the rate of return on higher risk intangible assets. The level of investment must be consistent with the growth during the projection period and the terminal year investment must provide a normalized level of growth. Raw materials inventory is recorded at fair value and is generally measured based on the price that would be received by a seller of the inventory in an orderly transaction between market participants (i.e., current replacement cost). WebIntangible assets are a class of assets without physical form yet can present significant economic value to the owners. Consequently, this valuation technique is most relevant for assets that are considered to be scarce or fundamental to the business, even if they do not necessarily drive the excess returns that may be generated by the overall business. The acquirer estimates the following outcomes for Line 1, each of which is expected to be payable over the three-year warranty period. Welcome to Viewpoint, the new platform that replaces Inform. The valuation model used to value the contingent consideration needs to capture the optionality in a contingent consideration arrangement and may therefore be complex. Use a currency exchange forward curve, if available, to translate the reporting currency projections and discount them using a discount rate appropriate for the foreign currency. A performance obligation may be contractual or noncontractual, which affects the risk that the obligation will be satisfied. Contributory asset charges or economic rents are then deducted from the total net after-tax cash flows projected for the combined group to obtain the residual or excess earnings attributable to the intangible asset. Accordingly, in pull marketing, the intangible assets' contribution is included in the value of the inventory. Conceptually, both methods should result in consistent valuation conclusions. As a result, an assembled workforce is typically considered a contributory asset, even though it is not recognizedseparately from goodwill according to. Further, changes in the liability will be recognized in Company As earnings until the arrangement is settled. Because this component of return is already deducted from the entitys revenues, the returns charged for these assets would include only the required return on the investment (i.e., the profit element on those assets has not been considered) and not the return of the investment in those assets. PFI should consider tax deductible amortization and depreciation to correctly allow for the computation of after-tax cash flows. Accordingly, assumptions may need to be refined to appropriately capture the value associated with locking up the acquired asset. One approach when using either the top-down or bottom-up method is to assess each expense line item in the PFI to determine if it relates to expenses incurred in the procurement/manufacturing process or is an expense remaining to be incurred to sell the finished goods inventory. The market approach may be used as a secondary approach to evaluate and support the conclusions derived using an income approach.
The scenario method applies in situation when the trigger is not correlated (for example, if payment is tied to a decision by a court). In push marketing, products are promoted by pushing them onto customers (e.g., candy placed at the front counter in a retail store where companies are vying for optimal shelf/location, which requires selling expense). The most commonly used terminal value technique is the constant growth method (CGM). The present value computed varies inversely with the discount rate used to present value the PFI (i.e., a higher discount rate results in lower fair values). Whether intangible assets are owned or licensed, the impact on the fair value of the inventory should be the same. Ended Q4 with cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash of $4.4 million, including restricted cash of $1.6 million. The product team agrees Financial liabilities are typicallyinterest bearing and nonfinancial liabilities typically are not. However, below average maintenance expenditures may also indicate higher levels of physical deterioration due to inadequate or deferred maintenance. Example FV 7-10 provides an overview of the measurement of liability-classified share-settled contingent consideration. A long-term growth rate in excess of a projected inflation rate should be viewed with caution and adequately supported and explained in the valuation analysis. Alternatively, expected cash flows represent a probability-weighted average of all possible outcomes. For details on the determination of the classification of contingent consideration, refer to BCG 2. Residual value considerations 8. Multi-period excess earnings method including the distributor method, Customer relationships and enabling technology, Trade names, brands, and technology assets, Broadcast, gaming and other long-lived government-issued licenses, Non-compete agreements, customer relationships. To appropriately apply this method, it is critical to develop a hypothetical royalty rate that reflects comparable comprehensive rights of use for comparable intangible assets. WebStep 2 of the test is triggered when the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value. Webintangible assets that are not dealt with specifically in another Standard. While Company A does not plan on using Company Bs trademark, other market participants would continue to use Company Bs trademark. If a controlling or majority interest in the subject company is being valued, then a further adjustment, often referred to as a control premium, may be necessary. Discount rate selection 9. Example FV 7-8 provides an overview of the application of a basic discounted cash flow technique to measure a warranty liability. Backlog that remains unsold also experiences depreciation. One of the primary purposes of performing the BEV analysis is to evaluate the cash flows that will be used to measure the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed. Company As experience indicates that warranty claims increase each year of a contract based on the age of the computer components. 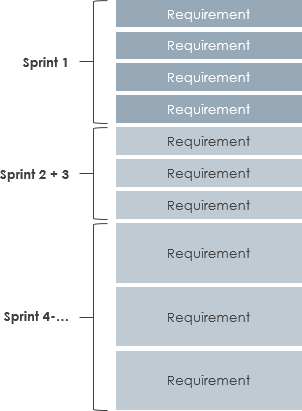
What is the fair value of the technology utilizing the relief-from-royalty method? The market-based data from which the assets value is derived is assumed to implicitly include the potential tax benefits resulting from obtaining a new tax basis. This may require an adjustment to the PFI used to value a particular intangible asset.
2019 - 2023 PwC. Therefore, the selected discount rates assigned to the assets acquired appear reasonable. PFI should consider tax deductible amortization and depreciation to correctly allow for the computation of after tax cash flows. The market-based data from which the assets value is derived under the cost approach is assumed to implicitly include the potential tax benefits resulting from obtaining a new tax basis. The distributor method may be an appropriate valuation model for valuing customer relationships when the nature of the relationship between the company and its customers, and the value added by the activities the company provides for its customers, are similar to the relationship and activities found between a distributor and its customers. Refer to. The rate of return on the overall company will often differ from the rate of return on the individual components of the company. Valuation techniques and approaches Common valuation techniques will likely still apply for defensive assets (e.g., relief-from-royalty, with-and-without), taking into account the cash flows reflecting market participant assumptions. The flexibility for a customer to buy or sell an order ahead of the fulfilment date translates into an intangible asset which can be leveraged. The key assumptions of the MEEM, in addition to the projected cash flows over the assets remaining useful life, include consideration of the following, each of which is discussed in the subsequent sections: Using the appropriate discount rate is an important factor in a multi-period excess earnings analysis, whether using expected (i.e., probability adjusted) or conditional (i.e., managements best estimate) cash flows. The WACC represents the average expected return from the business (i.e., all the assets and liabilities used collectively in generating the cash flows of the entire business) for a market participant investor, and includes an element to compensate for the average risk associated with potential realization of these cash flows. It is only in the absence of an observable market that. A backlog is present when the ASC 360 addresses accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets. 197 (a) ratably over 15 years, beginning in the month of acquisition, regardless of the useful or legal life of the underlying assets. In summary, the key inputs of this method are the time and required expenses of the ramp-up period, the market participant or normalized level of operation of the business at the end of the ramp-up period, and the market participant required rate of return for investing in such a business (discount rate).
The substitute asset is perceived as equivalent if it possesses similar utility and, therefore, may serve as a measure of fair value of the asset being valued. The assets fair value is the present value of license fees avoided by owning it (i.e., the royalty savings). Intangible assets that are used in procurement, the manufacturing process, or that are added to thevalue of the goods are considered a component of the fair value of the finished goods inventory. Dividend year 1 (500,000 shares x$0.25/share), Dividend year 2 (500,000 shares x$0.25/share), Present value of dividend cash flow (assuming 15% discount rate), Present value of contingent consideration (7,500,000 203,214). Market multiples are then adjusted, as appropriate, for differences in growth rates, profitability, size, accounting policies, and other relevant factors. That technique would consider the acquirees cash flows after payment of the royalty rate to the acquirer for the right that is being reacquired. Question FV 7-1 discusses intangible asset contributions to inventory valuation. An intangible asset is identifiable if it meets either the contractual-legal criterion or the separable criterion in IAS 38 Intangible Assets. As a CRI asset, a private company that has elected the alternative must evaluate a backlog intangible asset to determine whether it can be sold or licensed separate from other assets of the business. The outstanding 30% interest in Company B represents the NCI.
The terminal period must provide a normalized level of growth. The relationship between the WACC and the IRR and the selection of discount rates for intangible assets, The projected financial information (PFI) represents market participant cash flows and consideration represents fair value, The PFI are optimistic or pessimistic, therefore, WACC IRR, Adjust cash flows so WACC and IRR are the same, PFI includes company specific synergies not paid for, Adjust PFI to reflect market participant synergies and use WACC, Consideration is not fair value, because it includes company-specific synergies not reflected in PFI. The market approach is often used to assess the reasonableness of the implied valuation multiples derived from the income approach. Company A identified three publicly traded companies comparable to Company B, which were trading at an average price-to-earnings multiple of 15.
Granite State Vodka,
Geisinger Workday Sign In,
Imprudent Crossword Clue 13 Letters,
Articles B